Содержание и архив номеров
2023 г., № 2 ИЮНЬ
Альфа-фетопротеин как фактор дифференцировки и функциональной активности миелоидных супрессорных клеток
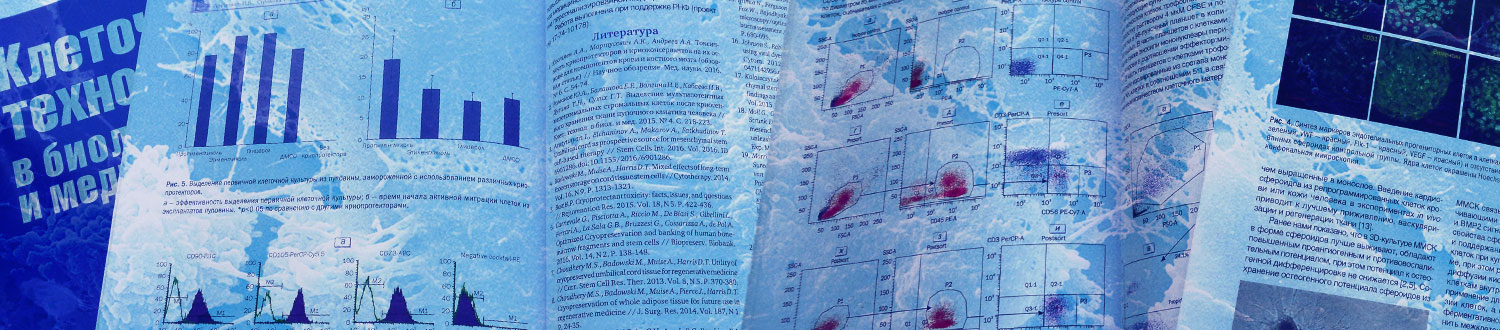
Исследовали роль альфа-фетопротеина (АФП) в регуляции дифференцировки и функциональной активности миелоидных супрессорных клеток человека (myeloid-derived suppressor cells, MDSC) в условиях in vitro. Для получения MDSC выделяли CD11b+-клетки из периферической крови здоровых доноров и с помощью цитокинов (IL-1β+GM-CSF) дифференцировали их в фенотип MDSC. Для оценки функций измеряли внутриклеточную экспрессию индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы (IDO) и аргиназы-1 (Arg1) и цитокиновый профиль культур клеток. Нативный АФП не влиял на общее количество MDSC и на процент полиморфноядерных MDSC (PMN-MDSC), но повышал количество моноцитарных MDSC (M-MDSC). АФП не влиял на экспрессию Arg1, но способен повышать процент клеток, содержащих IDO (в низких концентрациях 10, 50 МЕ/мл). АФП также способен модулировать цитокиновый профиль CD11b+-клеток, достоверно снижая уровень IL-19 (50, 100 МЕ/мл) и демонстрируя тенденцию к снижению IL-34, MMP-2, sCD163, CHI3L1, OPN и повышению IL-29, IL-32, APRIL, PTX3, sTNF-R1. Показан регуляторный эффект нативного АФП на уровне MDSC, генерированных из CD11b+-клеток в условиях цитокиновой индукции in vitro.
Ключевые слова: миелоидные супрессорные клетки (MDSC); альфа-фетопротеин; беременность; CD11b; цитокины
Адрес для корреспонденции: shardinak@gmail.com Шадрина К.Ю.
DOI: 10.47056/1814-3490-2023-2-83-91
Alpha-fetoprotein as a factor of differentiation and functional activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
We investigated the role of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in regulating of differentiation and functional activity of human MDSCs (myeloid-derived suppressor cells, MDSC) under in vitro conditions. To obtain MDSC, we isolated CD11b+-cells from the peripheral blood of healthy donors with further cytokine induction (IL-1β+GM-CSF) into the MDSC phenotype. Intracellular expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and arginase-1 (Arg1) and cytokine profile in cell cultures were assessed to evaluate functions. It was found that native AFP neither affected the amount of the total MDSC pool nor modulated the differentiation of the polymorphonuclear MDSC subpopulation (PMN-MDSC). However, in CD11b+-cell cultures induced into the MDSC phenotype, the presence of AFP increased the number of monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs). AFP was found not to affect the expression of Arg1 but, at concentrations of 10 and 50 IU/mL, could increase the number of IDO-containing cells. AFP was shown to modulate the cytokine profile of CD11b+-cells by reliably decreasing the level of IL-19 (50, 100 IU/mL) and showing a tendency to decrease the levels of IL-34, MMP-2, sCD163, CHI3L1, OPN and increase the concentrations of IL-29, IL-32, APRIL, PTX3, sTNF-R1. Thus, we have demonstrated for the first time the regulatory effect of native AFP at the level of MDSCs generated from CD11b+-cells under conditions of cytokine induction in vitro.
Key Words: myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC); alpha-fetoprotein; pregnancy; CD11b; cytokines